Pathologies
Bunions
A bunion is a protuberance on the side of the foot, in the area of the articulation of the big toe. The big toe, in some cases, could be diverted towards the smaller toes affecting their position.
What are the causes of bunions?
There generally exists a genetic predisposition, inheriting the type of foot that is predisposed to suffering from bunions. Flat or excessively flexible feet have a predisposition to developing bunions or other problems. Other causes could be traumatisms, rheumatoid arthritis and neurovascular diseases. In addition, in feet that have a certain predisposition, the shoe helps in the development of the bunion, reason why women, due to the type of footwear they use, suffer this illness more.
What are its symptoms?
Many times the pain does not correspond with the deformity; protruding bunions can be only slightly painful and small deformities can cause intense pains. Normally the pain comes from the rubbing of the footwear which causes reddening and inflammation and could develop into bursitis. With time the pain becomes more intense, making walking or even wearing footwear difficult. When the bunion has been developing for years the joint curvature forms a painful osteoarthritis which incapacitates. Bunions also affect the small toes, above all the toe adjacent to the big toe, which because of its curvature, begins to twist, this results in a hammertoe which frequently becomes complicated with a painful corn.
What treatments are suitable?
When the pain is not very intense, the best option is the conservative treatment. The change to wider and more comfortable footwear, with a low heel, is effective. Medication and anti-inflammatory cream help to eliminate the pain. When the conservative treatment is not effective and wearing footwear begins to become a problem, the surgical treatment is the best option. The longer the bunion is left without being operated on, the greater the arthritis and the greater the complication in surgery.
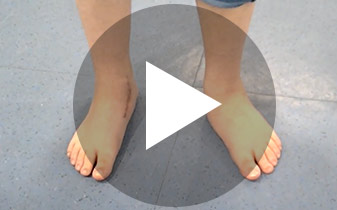
When and how to operate on the bunions? (hallux valgus)
At Clínica Benegas, with over seventeen years in the field and basing ourselves on our results, our advice is to operate on the bunions as soon as possible, whether because of pain or as soon as it begins to affect the adjacent toe. The lesser the deformity, the surgical technique is less aggressive and the results are also better.
At Clínica Benegas we use techniques that have been proven in the scientific community, and in the case of bunions, we consider it important to correct the deformity, not to cut or file down the bone, but to place the joint in its place to assure ourselves of good results in the future. The majority of cases can be operated on with local anaesthesia and in an outpatient visit.
After the surgery the patients walk out with post-surgery footwear, which they will wear for 10-15 days, after which they will be able to use soft and sports footwear, until finally normal footwear will be able to be worn when the scarring heals.
Hammertoes
Hammertoes are curved toes in the central joint, most frequent in the 2nd and 3rd toes. If the curvature is double, central and distal, they are claw toes. The curvature of the toe provokes greater rubbing of the footwear, forming a corn and consistent inflammation. It is important to point out that in this case the corn is not a skin problem, but that the skin is irritated by the protruding bone that rubs against the shoe.
What are the causes of hammertoe?
Flat feet, claw feet and very flexible feet have a predisposition to these problems. Other causes are excessively long toes, rheumatoid arthritis and neurovascular alterations. Women suffer this condition most because of the type of footwear and the use of stockings which compress the toes.
What are its symptoms?
The pain and corns are due to the friction of the footwear in that area. Continuous friction can cause reddening and inflammation and the formation of bursitis. In the first phase the deformity is flexible, but if it is not treated it can become more rigid, increasing the pain in the toe and even the sole of the foot. Hammertoes can also be due to bunions. If they are not treated in time, the curvature of the big toe can provoke the deformity of the other toes.
What treatments are suitable?
When the pain is moderate the conservative treatment can be effective. Use wider footwear which permits the mobility of the toes, crests and silicone pads also help. We do not advise the use of corn removers because they burn the good and bad tissue, possibly provoking ulcers and infections. When the conservative treatment does not work or footwear cannot be worn comfortably, surgical treatment is recommended.
When and how to operate on hammertoes?
At Clínica Benegas we advise to correct hammertoes in the first phase since the recovery is superior. The longer the surgery is delayed the greater the deformity becomes and the surgical technique used becomes more complex. When the curvature is flexible and reducible, a tendinous release is usually sufficient. When the curvature is rigid the toe needs to be realigned and sometimes a pin is placed to maintain the correction while it heals. These are operations that are done with local anaesthesia and the patient walks out with post-surgical footwear after the surgery. As the foot heals the patient returns to using normal footwear.
Onychocryptosis
It is a very frequent alteration in both children and adults which occurs when the edge of the nail digs into the surrounding skin. The most affected toe is usually the big toe.
What are the causes of onychocryptosis?
It can be caused by congenital alterations in the curvature of the nail, injuries, inappropriate nail cutting, footwear that is excessively narrow or digit deformities like bunions or hammertoes.
What are its symptoms?
The symptoms vary from moderate pain to inflammation and infection with pus drainage.
What treatments are suitable?
In normal cases the chiropodist will try to re-educate the nail so that it does not dig in, but in severe cases a definitive solution is sought which consists in a small surgical intervention which only eliminates the edge of the nail from its birth. This way it is prevented from digging in.
Heel pain
In a great percentage of the cases, the pain is due to the tension and/or inflammation of a ligament which runs through the sole of the foot from the toes to the heel. The ligament is called Plantar Fascia. Activities like running, remaining standing for long periods or an increase in weight can overload and inflame the Fascia. Changes in the way of stepping because of back, hip or knee pains or a flat foot with fallen arches can also cause pain. In older people the loss of the plantar fat pad is also a determinant. The pain is usually more frequent in only one heel although it can affect both. Men and Women are equally prone to this condition.
The x-ray of the heel can present a bone spur in the area where the Fascia inserts itself, although in half the cases with pain in the heel do not have a heel spur and 15% of adults without heel pain do have a heel spur. No direct relationship exists between having a heel spur and heel pains.
What is pain usually like?
Normally the pain appears when waking up from bed or after having remained seated for a while; the pain typically disappears as the person walks, although the pain may increase at the end of the day if the individual has walked a lot.
What treatments are suitable?
In the minor cases the following conservative measures can improve the pain:
- Avoid flat shoes and do not walk barefoot.
- Do not walk on irregular or soft surfaces such as grass or sand.
- Do not run or do jumping exercises. It is recommended to swim and cycle.
- Apply ice for 10 minutes.
If these remedies do not stop the pain, the foot must be stabilized with insoles to alleviate the Fascia. In the worst cases, a simple operation with local anaesthesia has very good results.
Alteration in children´s feet
Today, parents worried about the correct development of their children. Parents who wore corrective shoes or insoles want to know if their children need to wear them. Below we describe the most frequent alterations to evaluate what is considered normal or not.
FLAT FOOT OPERATION
In scientific terms it is called pronated foot. Certain flatness is normal but an excess can cause problems like bunions or heel pains for adults. The foot is normally inherited; it is normal for children up to 4-5 years old to have a certain grade of flatness due to the uterine position and the development of the legs. If your child is over 3-4 years old and has one foot different than the other or complains about cramps or excessive tiredness or if a family member has had flatfeet, an examination must be done with a specialist chiropodist.
Walk on tiptoes
Children who start to walk early usually tiptoe but must be corrected after 6 months. If it persists, it is convenient to consult with a specialist to discard neurological or skeletal-muscular problems.
Genu valgum
This forms part of the child’s normal development from 2 to 6 or 7 years old. If it is accompanied with pain or frequent falls, or one leg is different than the other, it is convenient to consult with a specialist.
Pigeon-toed
As in the other alterations, there exists a genetic component which conditions this process. A certain level of pigeon-towing can be considered normal, although the tendency usually disappears at 7-8 years old. If the child is born with the toes of the feet facing inwards and the foot adopts a “C” shape from the soles, it is recommended to consult a specialist as soon as possible to correct the curvature.
Bowlegs
Due to the uterine position, children are born with bowlegs. Normally this tendency disappears in 2-3 years. If the condition persists after 3 years, it should be consulted with a specialist.
Sports injuries - the foot in sports
When running, which occurs in the majority of sports, the load that the feet receive is multiplied by two or three times depending on the velocity. This overload needs special attention to avoid injuries.
The use of adequate footwear in sports activities is essential and the majority of times custom-made insoles are necessary for biomechanical control and to improve shock-absorbance.

Types of sports injuries
According to the type of sport and the movement carried out, there exists a greater predisposition to certain injuries.
Injuries because of continued flattening of the foot
The continuous flattening of the arches (overpronation) in continuous racing sports like marathon and cross-country running, among others, causes tension in the plantar fascia and in the tendons. Training shoes in a bad state and running on hard or irregular surfaces increase the possibility of injury. Injuries like plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis and periostitis are due to overpronation.
Injuries because of repeated jumps
When jumping, the loads are transmitted to the rear part of the foot, rather than to the entire sole. Sports like basketball, handball and volleyball increase the stress on the anterior part of the foot, able to cause stress fractures in the metatarsals.
Injuries because of lateral movements
Sports like tennis, racquetball... requires very fast changes in direction. These movements cause the articulations to suffer more, possibly provoking the tearing of ligaments. Sprained ankles of different grades are typical in these sports.